
Welcome to the world of stock trading! Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a beginner, this guide will help you navigate the complex world of stocks. From understanding the basics of stock trading to identifying profitable investment opportunities, we’ve got you covered. Let’s get started!
This guide was started when I started to learn about stock trading and is upgraded as I learn the tricks of the trade. In this guide, you will learn the following
Table of Contents
How do various assets and stocks trade in the Stock Market?
Before a company’s shares are traded in the stock market it has to go through several stages. The different stages of a business or startup, including the additional stages of funding are as follows.
- Ideation: The ideation stage is the first phase of a startup where the founders brainstorm and develop their business idea.
- Incubation: In this stage, the startup enters an incubation program where they receive support, mentoring, and resources to refine their idea and build a prototype.
- Seed funding: Seed funding is the initial capital provided to a startup to help them launch their business, build a minimum viable product (MVP), and conduct market research.
- Series A funding: Series A funding is typically the first significant round of funding a startup receives after seed funding. At this stage, the startup has developed its MVP and has demonstrated traction and potential for growth. Series A funding is used to scale up operations, build out the team, and further develop the product.
- Series B funding: Series B funding is the next round of funding that a startup receives after Series A. At this stage, the startup has achieved a significant amount of growth and has a clear path to profitability. Series B funding is used to accelerate growth, expand into new markets, and potentially acquire other companies.
- Series C funding: Series C funding is the next round of funding that a startup may receive after Series B. At this stage, the startup is a more mature company with a proven business model and is looking to further scale its operations, invest in new products or services, or expand internationally.
- Venture capital: Once a startup has developed its MVP and demonstrated traction in the market, it may seek funding from venture capitalists to scale up its operations and expand its market reach.
- Private placement: Private placement is a fundraising method in which a startup sells shares of its company to accredited investors.
- Initial Public Offering (IPO): An IPO is the process of offering shares of a private company to the public for the first time, which allows the company to raise capital from a wider pool of investors.
- Follow-on Public Offering (FPO): An FPO is a secondary public offering of shares by a company that has already gone public, usually to raise additional capital for expansion or other purposes.
These stages of funding are not necessarily linear, and a startup may skip or overlap them depending on its unique circumstances and needs.
There may be other stages of funding that a startup may go through, depending on the industry and the startup’s unique circumstances. Here are a few additional stages of funding:
- Pre-Seed Funding: Pre-seed funding is the earliest stage of funding, which occurs before seed funding. This funding round is typically used to fund the initial research and development of the business idea and is often provided by friends and family, angel investors, or incubators.
- Mezzanine Financing: Mezzanine financing is a form of debt financing that typically occurs between the later stages of venture capital and before an IPO. This funding round may involve a mix of debt and equity financing and is often used to fund the growth of a startup while the company prepares for an IPO.
- Bridge Financing: Bridge financing is a short-term funding solution that bridges the gap between two rounds of funding. This type of funding is typically used to cover expenses until the next funding round is secured.
- Strategic Investment: A strategic investment is an investment made by a corporation or investor that has a strategic interest in the success of the startup. In addition to providing funding, strategic investors may also provide access to resources, expertise, and networks that can help the startup grow.
Again, it’s important to note that these stages of funding are not necessarily linear, and a startup may skip or overlap them depending on its unique circumstances and needs.
What is the difference between the stock market and the share market?
The terms “stock market” and “share market” refer to the same thing, which is the marketplace where stocks (or shares) of publicly traded companies are bought and sold.
What are the different types of markets?
- Primary market: A primary market is where securities or stocks are created and sold for the first time called an IPO. In this market, companies raise funds by issuing new stocks or bonds. The buyers of these securities are institutional investors, and retail investors, such as mutual funds, insurance companies, and pension funds. These are usually not sold through stock exchanges but need to be applied for purchase through a bank account or broker account by parking margin money. If the IPO is allotted then the money would be debited the money would be released.
- Secondary market: A secondary market is where previously issued securities are bought and sold. This market is where investors trade stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments through various stock exchanges. The stock exchanges, such as the NSE, BSE, New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), and Nasdaq facilitate such transactions of secondary markets.
- Cash market: A cash market is a market where financial instruments are traded for immediate delivery. In this market, trades are settled in cash, and there is no future delivery date. The stock market is an example of a cash market.
- Derivatives market: A derivatives market is where financial instruments derive their value from underlying assets such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. Derivatives include options, futures, swaps, and forwards. These instruments are used for hedging, speculation, and arbitrage. Initially, the investors used it to hedge their other positions. Lately, traders started it for speculation. Usually, these financial instruments have an expiry and they could be weekly or monthly.
- Debt market: A market where fixed-income securities such as bonds, notes, and bills are traded. These securities represent loans made by investors to governments, corporations, or other entities.
- Equity market: A market where ownership shares of companies, such as common stocks, preferred stocks, or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), are traded.
- Cryptocurrency market: A market where digital currencies, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, are traded.
- Foreign exchange market: A market where currencies of different countries are bought and sold, which involves exchanging one currency for another at an agreed-upon price.
- Commodity market: A market where commodities, such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products like wheat, corn, and soybeans, are bought and sold. These markets allow producers and consumers of these commodities to hedge against price fluctuations and manage risks. The commodity market can be further subdivided into soft commodities, such as coffee, cocoa, and sugar, and hard commodities, such as metals and energy.
Who are all the different market players in the stock market
The stock market is made up of various types of players who interact with each other to buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. Here are some of the main players:
- Investors: Investors, both individual and institutional, participate in the stock market by buying shares in publicly listed companies.
For example, individual investors may buy shares in companies like Reliance Industries or Tata Consultancy Services, while institutional investors like mutual funds or pension funds may hold shares in multiple companies. - Traders: Traders, both individuals and firms, participate in the stock market by buying and selling shares frequently.
Day traders, for example, may buy and sell shares in a single day, while high-frequency trading firms use algorithms to execute trades automatically. - Brokers: Stockbrokers act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers of shares, executing trades on behalf of their clients.
Some popular stockbrokers in India include Zeroadha, Upstox, ICICI Securities, Kotak Securities, and HDFC Securities. - Market makers: In India, market makers are typically large financial institutions like ICICI Bank or HDFC Bank that facilitate trading by buying and selling shares on their behalf to ensure there is always a buyer or seller for a particular stock.
- Investment bankers: Indian investment banks help companies issue new shares of stock or raise capital through other means, such as debt offerings or mergers and acquisitions. Examples of Indian investment banks include Kotak Investment Banking, ICICI Securities, and Axis Capital.
- Regulators: The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the primary regulatory body that oversees the Indian stock market, enforcing regulations to protect investors and maintain market integrity.
- Financial analysts: Indian financial analysts provide research and analysis on individual companies and industries to help investors make informed decisions. Some prominent Indian financial analysts include Nimesh Shah, Motilal Oswal, and Prabhudas Lilladher.
- Stock exchanges: In India, the two major stock exchanges are the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). These exchanges provide physical or electronic marketplaces where shares are bought and sold.
What are the different types of traders involved in assets/stock trading
There are several types of traders in the financial markets, including:
- Day Traders: These traders buy and sell securities within the same trading day, aiming to take advantage of short-term price movements.
- Swing Traders: Swing traders hold positions for several days to a few weeks, aiming to profit from medium-term price movements.
- Position Traders: Position traders hold positions for months to years, aiming to profit from long-term price movements.
- Scalpers: Scalpers are day traders who aim to make profits by making many quick trades within a single trading day, taking advantage of small price movements.
- Algorithmic Traders: Algorithmic traders use computer programs to execute trades based on predetermined rules and algorithms.
- High-Frequency Traders: High-frequency traders use computer algorithms to make trades in milliseconds, taking advantage of small price discrepancies.
- Institutional Traders: Institutional traders work for large financial institutions and trade with large amounts of capital, often using complex strategies to manage risk and generate returns.
- Retail Traders: Retail traders are individual traders who trade with their own money and typically have smaller account sizes compared to institutional traders.
- Option Traders: Options traders trade options contracts, which give them the right to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and time. Option traders use a variety of strategies to profit from price movements in the underlying asset, including buying or selling options, and investors can also use options to hedge other positions.
- Future Traders: Futures traders who trade futures contracts, which are agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price and time in the future. Investors can also use futures to hedge other positions.
- Commodities Trader: A commodities trader is an investor who trades in commodities, such as crude oil, gold, agricultural products, and other raw materials. Commodities traders use a variety of strategies to profit from price movements in the commodity markets, including buying and selling commodity futures contracts, trading commodity options, and investing in commodity ETFs or mutual funds.
- Forex Trader: A Forex (foreign exchange) trader is an investor who trades in currency pairs, buying and selling one currency against another to make a profit from the exchange rate fluctuations. Forex traders use a variety of strategies to profit from price movements in the currency markets, including technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and algorithmic trading. Forex trading requires a solid understanding of currency market dynamics, global economic events, and monetary policy, as well as the risks involved in trading Forex, such as high leverage and volatility.
It’s important to note that these categories are not mutually exclusive, and traders may use a combination of strategies and timeframes depending on their goals and risk tolerance.
What are the different types of brokers in India?
In India, there are several types of brokers who provide services to investors in the stock market. Here are some of the main types of brokers in India and examples of firms that offer these services:
- Full-service brokers: Full-service brokers offer a wide range of services, including investment advice, research, financial planning, and portfolio management. They typically charge higher fees and commissions than other types of brokers. Examples of full-service brokers in India include ICICI Securities, HDFC Securities, and Kotak Securities. It can be expensive for beginners but for traders trading in huge volumes, it can be cheaper than discount brokers as the brokerage can be negotiated against a minimum guaranteed transaction.
- Discount brokers: Discount brokers offer basic trading services, such as buying and selling stocks, at a lower cost than full-service brokers. They typically do not offer investment advice or other services. Examples of discount brokers in India include Zerodha, Upstox, and 5paisa. Discount brokers are the best for beginners.
- Online brokers: Online brokers provide trading services through an internet-based platform. They offer lower fees and commissions than full-service brokers and may provide research and other investment tools. Examples of online brokers in India include Sharekhan, Angel Broking, and Edelweiss.
- Institutional brokers: Institutional brokers provide trading services for large institutional investors, such as mutual funds, pension funds, and hedge funds. They offer specialized services such as block trading, which involves buying or selling a large number of shares at once. Examples of institutional brokers in India include Axis Securities, Motilal Oswal, and IIFL Securities.
What is the relation between a bank account, trading account, demat account, and stock exchange?
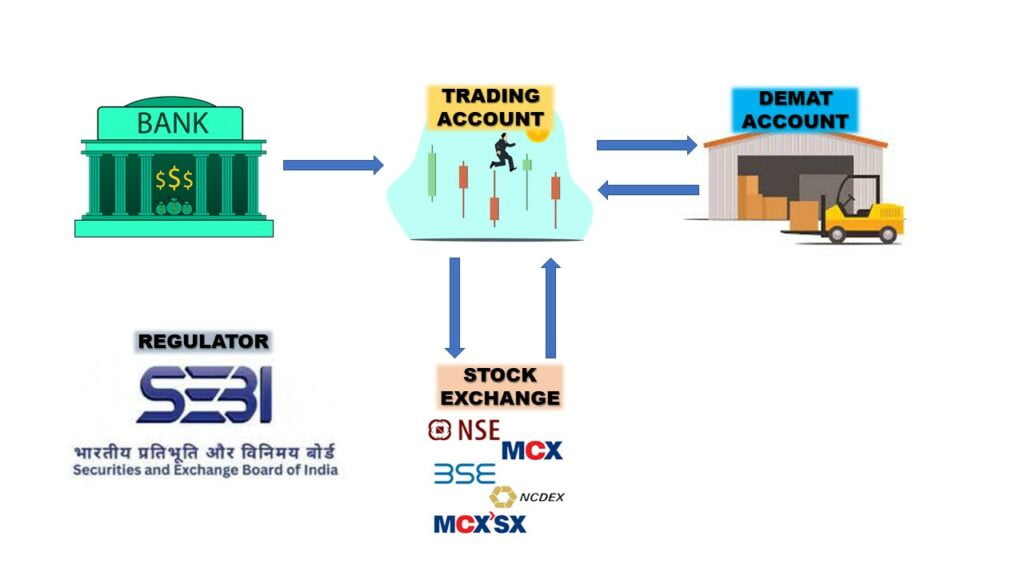
Demat account stands for a dematerialized account because shares are stored in electronic format. In India, there are only two companies that provide demat accounts. They are
A trading account is an account maintained with a broker like Zeroadha, upstox…etc. Trading accounts and demat accounts are tightly connected for ease of trading. One can buy a share and send it to their demat account as well and they can also pull the stock from a demat account and sell it in the open market through their trading account without even opening their demat account.
A Bank account is used to fund the trading account for trading and investing. It is also used for the withdrawal of funds from a demat account. Nowadays all three accounts can be opened in one go since all big banks provide their broking services.
A Stock Exchange is a market where shares are exchanged with the help of a trading account. In India NSE and BSE deals with stock and derivatives while MCX deals with commodities.
SEBI is the regulator in India that ensures the smooth functioning of all the players.
What are the different types of stock exchanges in India?
There are two major stock exchanges in India:
- National Stock Exchange of India (NSE): It was founded in 1992 and is located in Mumbai. It is the largest stock exchange in India in terms of market capitalization and trading volume. It offers trading in equities, derivatives, and debt securities.
- Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): It was founded in 1875 and is also located in Mumbai. It is the oldest stock exchange in Asia and offers trading in equities, derivatives, and debt securities.
Apart from these, there are also some regional stock exchanges in India such as Calcutta Stock Exchange, Madras Stock Exchange, and Ahmedabad Stock Exchange, but they have relatively smaller trading volumes and are not as active as NSE and BSE.
Can we buy shares in NSE and sell in BSE and vice-versa?
The answer is YES and NO. The delivery of stocks takes 2 days to be deposited in our demat account. This is also called T+2. After delivery into our demat account, one can sell in any exchange irrespective of where it is purchased. However, the stocks can only be sold in the respective exchanges during these T+2 days.
NSE vs BSE which is better?
NSE hosts 2000 stocks while BSE hosts 5000 stocks but the trading volume of NSE in the cash market is 80% while in the derivative market is 90%. Therefore the liquidity is high in NSE.
For intraday traders and derivative traders, NSE is better because of liquidity. High liquidity helps in
- Better spreads
- Lower Slippage
- Easy entry and exit
Investors interested in investing in mid-cap or small-caps may look at both exchanges as it is possible many stocks may not be available in NSE but can be purchased through BSE.
What is NIFTY and SENSEX?
Nifty and Sensex are the two primary stock market indices of the Indian stock market.
The Sensex or sensitive index (also known as the BSE Sensex) is an index of the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and is considered the benchmark index of the Indian stock market. It is a collection of the 30 most actively traded stocks listed on the BSE. The Sensex is a market capitalization-weighted index, which means that the weight of each stock in the index is determined by its market capitalization.
On the other hand, the Nifty (also known as the NSE Nifty or Nifty 50) is an index of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and comprises the 50 most actively traded stocks listed on the NSE. The Nifty is also a market capitalization-weighted index, and the weight of each stock in the index is determined by its market capitalization.
The companies included are rebalanced twice a year where some companies are removed and some are added, to accurately represent the Indices.
Both the Sensex and Nifty are used as barometers of the overall performance of the Indian stock market. The movements of these indices are closely watched by investors and market analysts as they provide a broad understanding of the direction of the Indian stock market.
Every country has its indices to understand its stock markets. Here is a list of some of the major stock market indices for the world’s largest economies:
- United States – S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Nasdaq Composite
- China – Shanghai Composite, Shenzhen Composite, Hang Seng China Enterprises Index
- Japan – Nikkei 225, Topix
- Germany – DAX, MDAX
- United Kingdom – FTSE 100, FTSE 250
- India – BSE Sensex, NSE Nifty 50
- France – CAC 40
- Brazil – Bovespa
- Canada – S&P/TSX Composite
- South Korea – KOSPI, KOSDAQ
- Australia – S&P/ASX 200
- Russia – MOEX Russia Index
- Italy – FTSE MIB
- Spain – IBEX 35
- Mexico – IPC
- Indonesia – Jakarta Composite Index
- Netherlands – AEX
- Turkey – BIST 100
- Saudi Arabia – Tadawul All Share Index
- Switzerland – Swiss Market Index (SMI)
What is an Index Fund?
Index funds are mutual funds that closely match the stock of popular indices. The fund manager simply picks those stocks that are part of these indices. Because of this, the expense ratio is one of the lowest in such mutual funds when compared with other mutual funds where the fund manager picks stock after rigorous analysis. Index funds are very popular among investors including Warren Buffet because of above-average returns and high probability of asset appreciation.
Technical Analysis
Why technical analysis is to be studied for success in the stock market
- It helps in identifying the entry and exit points for both traders and investors. In other words, it signals when to buy an asset when to sell an asset, and what the stop loss would be.
- It is to identify the logic behind the chart pattern
- It is used to identify a short-term trading opportunity while long-term investors use fundamental analysis
- It helps visualize and analyze the forces behind the market causing a change in the price of stock/commodities
- It helps to predict price movement
- It also helps identify where institutional investors put and withdraw their money (a.k.a smart money) so that retail investors can copy such trades
- It can be applied across every asset class like stocks, commodities…etc
- It is relevant across all asset classes like equity, commodities, currencies…etc while the fundamental analysis is asset specific i.e. fundamental analysis of commodities is different from equities.
Top 5 books to learn technical analysis
- Popular with Professional Traders – Technical Analysis Explained, Fifth Edition: The Successful Investor’s Guide to Spotting Investment Trends and Turning Points by Martin J Pring
- Best for Beginners – Technical Analysis of the Financial Markets: A Comprehensive Guide to Trading Methods and Applications by John J. Murphy
- Old but Gold –Technical Analysis of Stock Trends by Robert D. Edwards and John Magee
- Best for CandleStick Charts – Japanese Candlestick Charting Techniques: A Contemporary Guide to the Ancient Investment Techniques of the Far East, Second Edition by Steve Nison
- Best Ready Reference Guide – Encyclopedia of Chart Patterns: 225 (Wiley Trading) by Thomas Bulkowski
Top 5 Books for Indian Traders
- Ideal for Beginners – Trading in the Zone: Master the Market with Confidence, Discipline, and a Winning Attitude by Mark Douglas
- To learn strategies – Market Wizards: Interviews with Top Traders by Jack D. Schwager
- Reminiscences of a Stock Operator: With New Commentary and Insights on the Life and Times of Jesse Livermore by Edwin Lefèvre
- For Trading Psychology –Thinking, Fast and Slow by Daniel Kahneman(Nobel Laureate)
- Trading for a Living: Psychology, Trading Tactics, Money Management by Alexander Elder
Introduction to Technical Analysis
Assumptions in Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is based on several key assumptions, including:
- Market trends: Technical analysis assumes that markets move in trends that can be identified and analyzed to make trading decisions.
- Price discounts everything: Technical analysts assume that all market information, including economic, political, and social factors, is reflected in the current price of an asset.
- History repeats itself: Technical analysts believe that past price patterns and market behaviour tend to repeat themselves and that these patterns can be used to predict future price movements.
- Market psychology: Technical analysis assumes that market participants are not always rational and that their emotions and behaviour can be reflected in price movements.
- Resistance and support levels: Technical analysis assumes that price levels where an asset has previously found support or resistance can provide valuable information about future price movements.
It’s important to note that while technical analysis can be a useful tool in trading, these assumptions are not always accurate, and no trading strategy can guarantee success. Traders should use technical analysis in conjunction with other forms of analysis and have a solid understanding of the risks involved in trading.
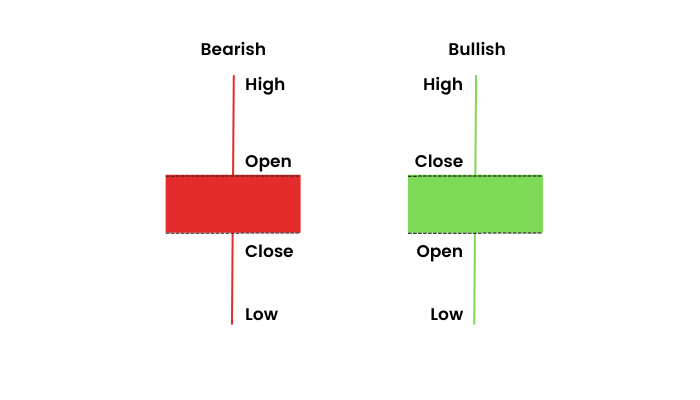
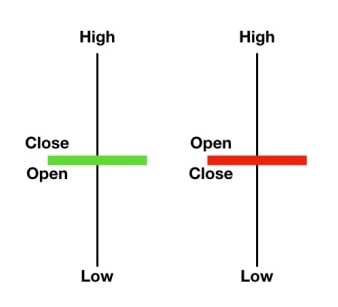
OHLC
OHLC stands for Open, High, Low, and Close, which are the four most important prices in financial trading. The OHLC chart is a common way of representing the price movement of an asset over a given period.
- Open refers to the price of the asset at the beginning of the trading period
- Close refers to the price of the asset at the end of the trading period
- High represents the highest price the asset reached during the trading period
- Low represents the lowest price the asset reached during the same period
Chart Pattern
Trade charts are graphical representations of financial data that display the price movements of assets over a given period. There are many types of trade charts like lines, bars, candle sticks…..etc but the most useful one is the Japanese Candlestick Chart. The line chart is formed by connecting the closing price of the asset, while the bar chart is the same as the Japanese candle chart but without user-friendliness.
Japanese Candlestick charts: These charts use candlestick-shaped symbols to represent each data point. The body of the candlestick represents the opening and closing prices, while the “wicks” or “shadows” at the top and bottom of the body represent the high and low prices.
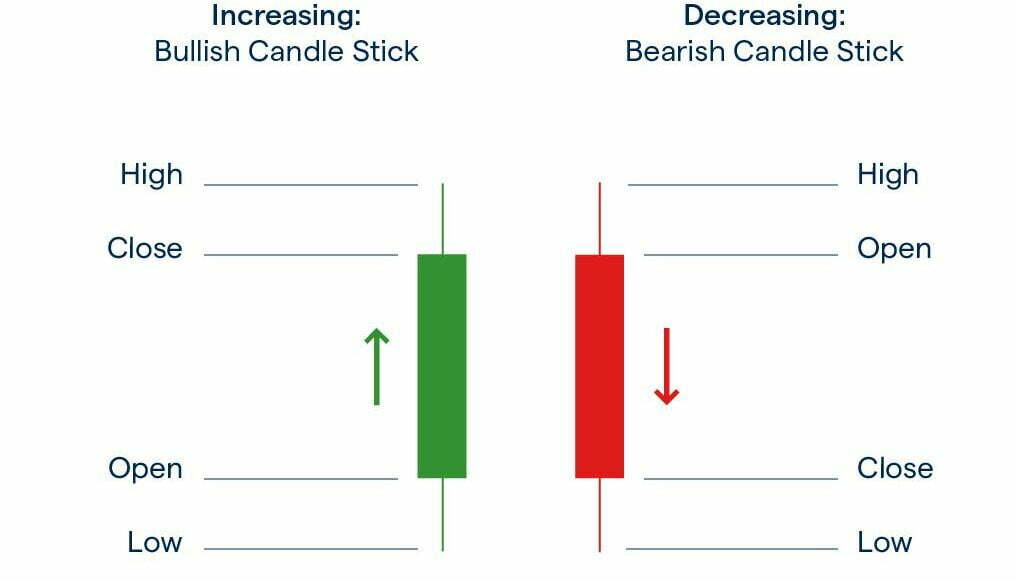
- There are two types of candlesticks – Bullish and Bearish candlesticks
- When the Close > Open = Bullish Candle
- When the Open > Close = Bearish Candle
Time Frames
- Time frame is very important for success in trading and hence should be chosen carefully.
- Some important frames are
- Monthly Charts – 12 candles per year
- Weekly Charts – 52 candles per year
- Daily Chart or End of the Day Chart – 252 per year
- Intraday Chart (only important timeframes)
- 30 min – 12 candles per day
- 15 min – 25 candles per day
- 5 min – 75 candles per day
Candle Stick Patterns
Candlestick pattern helps to predict market movements. The patterns are based on the assumption that “History repeats itself”. The pattern can be of two types – Single and Multiple candlestick patterns.
Single Candle Stick Pattern
- Marubozu
- Bullish Marubozu
- Bearish Marubozu
- Spinning Tops
- Doji
- Paper Umbrella
- Hammer
- Hanging Man
Multiple Candle Stick Pattern
- Engulfing pattern
- Bullish Engulfing
- Bearish Engulfing
- Harami
- Bullish Harami
- Bearish Harami
- Piercing Pattern
- Dark Cloud Cover
- Morning Star
- Evening Star
There are 3 assumptions specific to candlestick pattern
- Buy strength and sell weakness
- Be flexible with patterns – quantify and verify
- Look for a prior trend
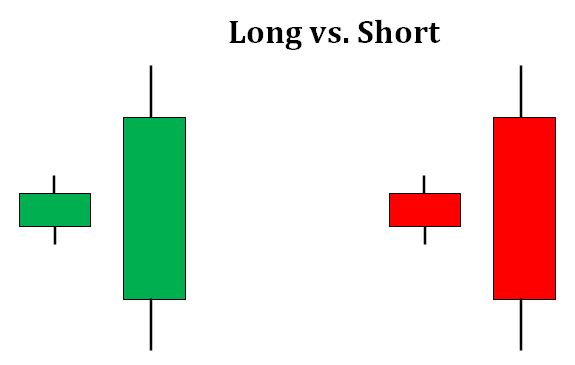
Long Verses Short Candle
- Long candle = Intense buying and selling
- Short candle = Subdued buying and selling
Single Candle Stick Pattern
Marubozu
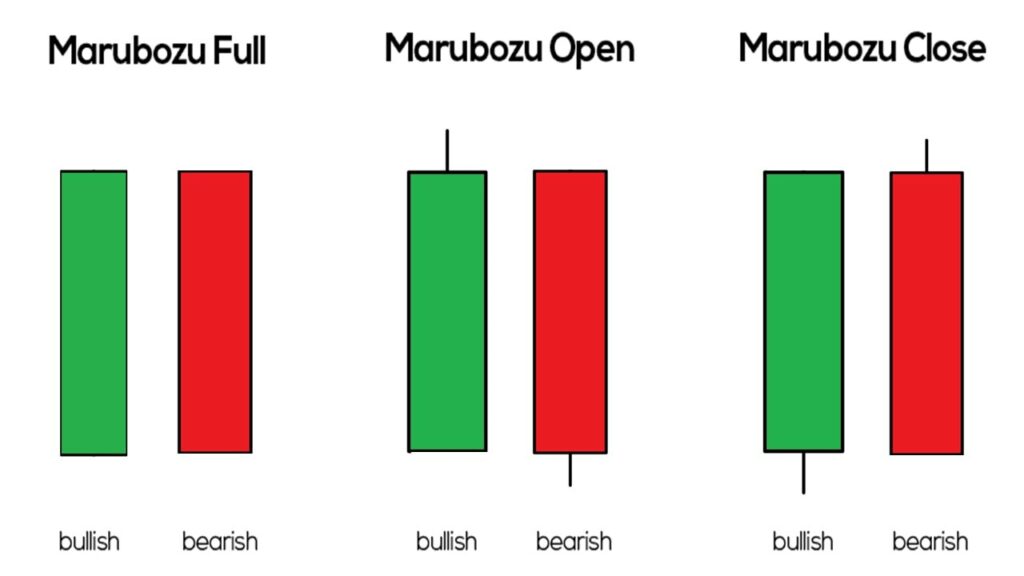
- It is the Japanese word for dominance
- It is the only candlestick that violates the 3rd rule ” Look for prior trend ” assumption i.e. it can be a trend reversal or trend continuation candle.
- The candle is usually formed in a longer time frame i.e daily, weekly, or monthly
- Here the colour of the candle sticks matters as it indicates Bullishness or Bearishness
- Characteristics
- Long full body in the bullish candle – meaning bulls were ready to buy at every price point to the extent the candle closed at high and opened at low
- Long full body in the bearish candle – meaning the bear was ready to sell at every price point to the extent the candle closed at low and opened at high
- Bullish Marubozu indicates bullishness
- Buy at the closing price
- Stoploss at the low of Marubozu
- Bearish Marubozu indicates bearishness
- Sell around the closing price
- Stoploss at the high of Marubozu
- Aggressive traders can trade on the same day as the pattern forms
- Risk-averse traders can wait until the end of the next day and confirm it obeys the 1st rule ” Buy in strengths and sell in weakness “
- Abnormal candle length should not be traded
- Short candle indicates subdued activity
- Long candle indicates extreme activity, stop-loss can be very steep
The spinning Top
- Characteristics
- Small real body – Indicates the open and close price is close to each other
- Long upper shadow – Attempt by bulls to raise the price but failed
- Long lower shadow – Attempt by bears to crash the price but failed
- Upper and Lower shadow of equal size – Conveys indecision in the market i.e the bulls and bears made an attempt to control the market but failed
- The colour doesn’t matter
- It doesn’t give any entry or exit points
- A spinning top is the “Calm before the Storm ” – It can mean the continuation or reversal of a trend
- Continuation of Trend – In a trending market the Bulls or Bears could be consolidating their position for another round of buying or selling to raise or crash the price
- Reversal of Trend – In a trending market the Bulls or Bears are exhausted and giving way for Bears or Bulls respectively
- The chances of both these events taking place are 50% each
- A spinning top means the market can go in any direction and therefore it is a point to exit from the market.
- If the position is in profit then one can book the profit and exit the trade completely or partially
- If the position is in loss one can exit and further limit the loss completely or partially
- To sum up, in the case of the spinning top, the market is in the confusion or indecision stage. Therefore one should minimize their size or exit completely. For example, one can book a profit on 50% of their position and wait for the market to react. If it moves in their favourable direction then they can continue booking profits in their remaining 50% of holdings. If the market moves in the direction of a disadvantage then one can exit the market completely and book a net profit.
The Dojis
- Doji’s are similar to spinning tops except they don’t have real bodies.
- The open and close prices are the same or very close
- Doji means “same thing” in Japanese
- Here the colour of the candle doesn’t matter like the spinning top
- Whatever is true with the spinning top is true with Doji as well
Paper Umbrella
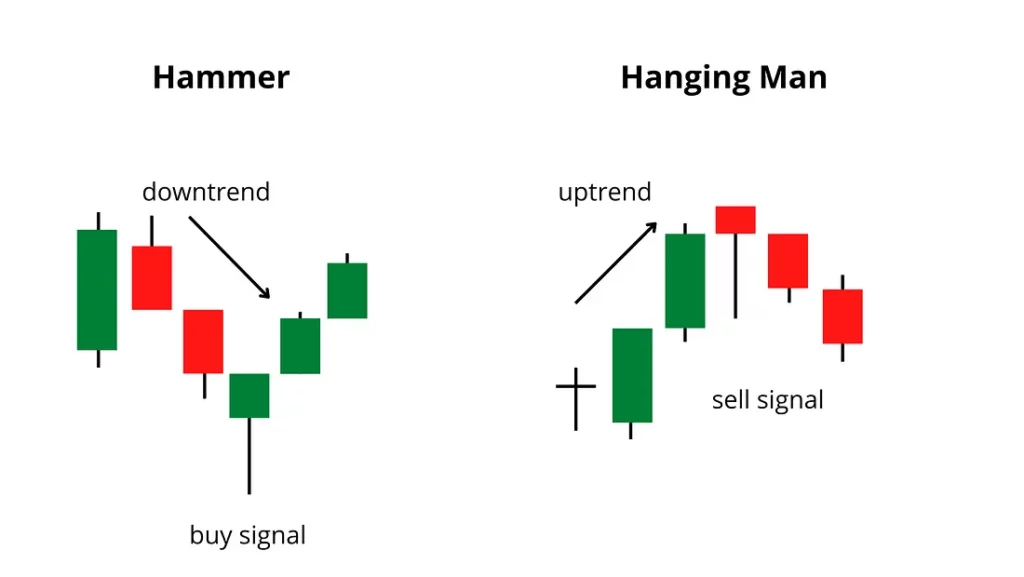
- Characteristics
- Long lower shadow
- Small upper body
- Shadow to real body ratio min 2:1
- The longer the shadow more bullish or bearish the candle
- The Bullishness of Hammer is more reliable than the bearishness of the Hanging Man
- It indicates the reversal of a trend
- It has two names depending on where it appears
- Top of the Chart – Hanging Man – Bearish
- Colour doesn’t matter
- The prior trend should be an uptrend
- The uptrend is broken when the candle makes a low and closes near open making a small body.
- The open and close should be near i.e 1-2% range
- It suggests short entry or sell entry
- Risk takers can short or sell on the same day irrespective of the candle colour
- Risk-averse can short or sell on close of the following day if the candle is red
- High of the candle acts as a stop-loss
- Bottom of the Chart – Hammer – Bullish
- Colour doesn’t matter but usually Green
- The prior trend should be a downtrend
- The downtrend is broken when the market closes near the high of the day meaning bulls entered the market
- The open and close should be near i.e 1-2% range
- It suggests long entry or buy entry
- Risk takers can buy on the same day irrespective of the candle colour
- Risk-averse can buy on the following day if the candle is green
- Low of the candle acts as a stop-loss
- Top of the Chart – Hanging Man – Bearish
The Shooting Star
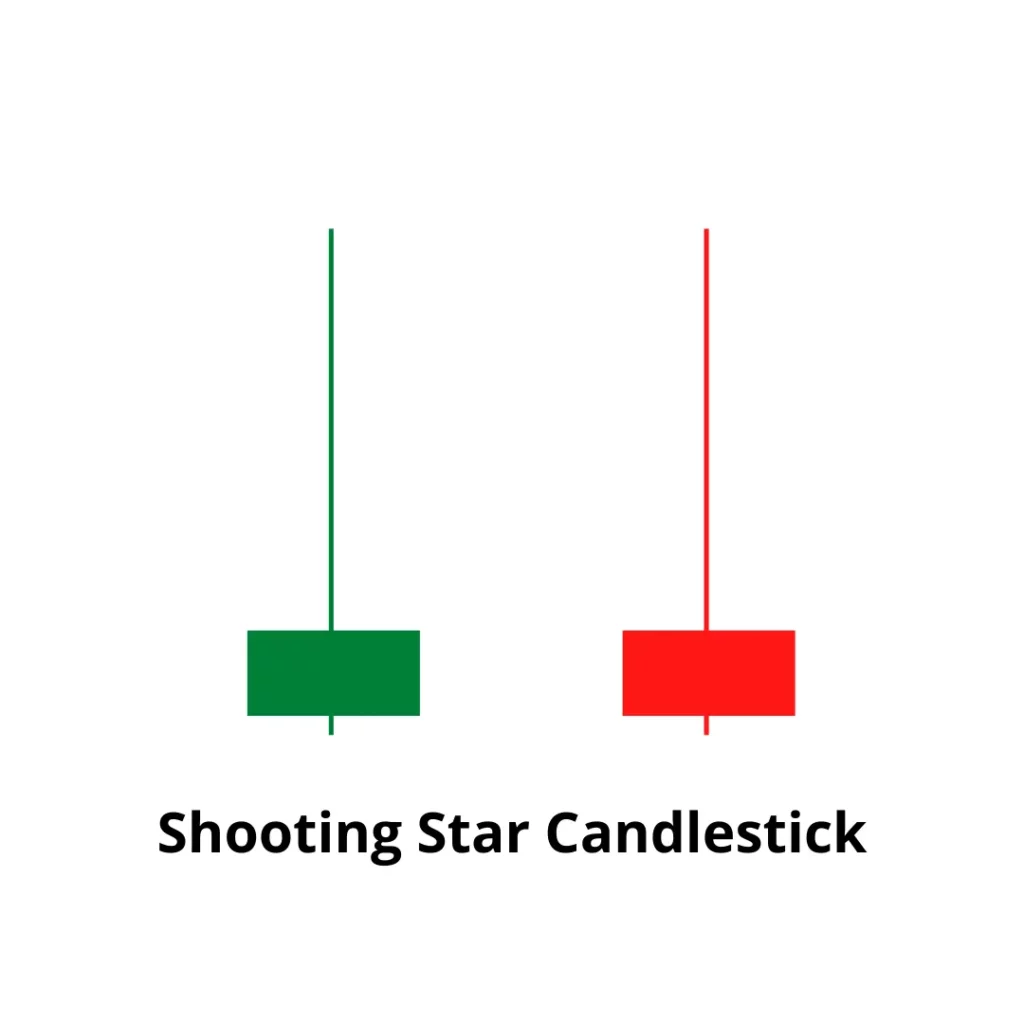
- Characteristics
- Looks like an inverted paper Umbrella
- It has a long upper(at least 2 times the body) and a small body
- Colour doesn’t matter – But a red candle means the signal is more reliable
- It is a bearish pattern
- The prior trend should be bullish
- Action
- The asset should be short or sold
- Stoploss at the high of the candle
Multiple Candle stick pattern
A single Candle stick pattern needs only one trading session to identify trading opportunities while a Multiple candle stick pattern needs more than one trading session to identify a trading opportunity.
The Engulfing Pattern
- Characteristics
- Needs two trading session
- Small candle on day 1 & Relatively larger candle on day 2 that engulfs the small candle
- There are two candles depending on where the pattern appears
- Bullish Engulfing – Bottom end of the trend
- Day 1 Small Candle should be Red only
- Day 2 Engulfing Candle should be Green only
- The prior trend should be a downtrend
- The action should be to buy the asset
- The Stop loss is the low of day 2
- Bearish Engulfing – Top end of the trend
- Exactly opposite of Bullish Engulfing
- The action is to short or sell the asset
- The stop loss is the high of day 2
- Bullish Engulfing – Bottom end of the trend
- The risk taker can take the trade on day 2 while the risk-averse may take the trade on day 3 after confirming the expected trend.
The piercing pattern
- It is similar to Bullish Engulfing but engulfing is between 50% to 100%.
- Everything else is the same as Bullish Engulfing
Dark Cloud Cover
- It is similar to Bearish Engulfing but engulfing is between 50% to 100%
- Everything else is the same as Bearish Engulfing
The Haramai Pattern
- It is a Japanese word meaning “Pregnant”
- The pattern is formed over 2 trading sessions
- 1st candle is usually longer than the previous candle
- Trend reversal is possible after this pattern therefore there are two types based on where the pattern appears. They are
- Bullish Harami – Appears at the bottom of the chart
- Bearish Harami – Appears at the top of the chart
- The stop loss is the highest high of either of the trading session in the case of Bearish Harami
- The stop loss is the lowest low of either of the trading sessions in the case of Bullish Harami.
The Morning Star
- The pattern is made over 3 trading sessions
- It appears at the bottom end of a downtrend
- It is a downtrend reversal pattern
- Characteristics
- Day1 should be a red candle
- Day2 should be a gap-down opening
- Day2 should form a Doji or Spinning Top
- Day3 should be Gap up and the current market price should be higher than the opening of Day1
- Here both risk-taker and risk-averse can initiate long trade on Day 3 itself
The Evening Star
- It is the reverse of the Morningstar but it is formed at the top of the uptrend.
Support and Resistance
- Support in the market refers to a price level at which a financial asset is expected to stop falling due to the presence of buyers who are willing to purchase the asset at that price.
- Resistance in the market refers to a price level at which a financial asset is expected to stop rising due to the presence of sellers who are willing to sell the asset at that price.
A candlestick pattern can help find the right entry and SL points while the support and resistance will help find the predefined target or exit points.
- For a long trade, the immediate resistance level may be the target.
- For a short trade, the immediate support level may be the target.
How to find Support and Resistance?
- Load data points
- For Swing Trade – 12-18 months of data points give long-term S&R
- For Intraday and BTST trades – 3-6 months of data points give Short-term S&R
- Identify at least 3 price action zones – These points are identified by any of the below behaviour
- Price hesitated to move up
- Price hesitated to move down
- A sharp reversal of a trend
- Horizontally align the price action zones
- Identify at least 3 price action zones at the same level and align them
- The more distance between two price action zones the more accurate the S&R
Volumes
- Volumes are used to confirm trends and patterns
- It is the means to find out how other participants perceive the market
- It indicates how many shares are exchanged over a given period of time
- If the price is increasing or decreasing steadily and the volumes are also increasing then it signals strong bullishness or bearishness respectively.
- If the price is increasing or decreasing steadily and the volumes are not changing much then it signals weak bullishness or bearishness respectively and hence the trade may not be worth taking.
What are deliverables
- Deliverable quantity is the number of shares delivered.
- Delivery % = Deliverable Quantity / Traded Quantity
- Delivery is a measure of Bullish confidence in the stock
- It can be used for finding Bullish strong vs Bullish weak stocks
- Logic behind analysis
- There are mainly two types of trade – Delivery based and Non-Delivery based
- In non-delivery-based trade, one can see their profit and loss in real time and exit when required
- In delivery-based trade, the investor needs to hold an overnight position. The profit or loss can be huge due to gap-up or gap-down. The investors take delivery only when the Bullish conviction is high. So the higher the delivery higher the Bullish Confidence.
- To be used with other technical indicators
to be continued